Neurological disease is unfortunately exceptionally widespread. The United Nations estimates that 1 in 6 people globally suffers from a neurological disorder. Across the globe, that adds up to literally billions of people.
The good news for Floridians and Americans more broadly is that we have some of the best tools of any nation to effectively treat many neurological conditions, both in children and adults. Some neurological conditions are entirely curable, while others can be managed with the right interventions.
Here, we’ll cover what exactly we mean when we talk about “neurological conditions” and what that means for the patients we treat.
A Brief Overview of the Nervous System
The nervous system is the primary control mechanism for bodily functions, the main regulatory system to maintain homeostasis (constant healthy conditions in the body), and the central communication system for receiving, distributing, and processing information.
Needless to say, given its vital roles, maintaining a healthy and functional nervous system is critical for good health.
The two primary components of the nervous system are:
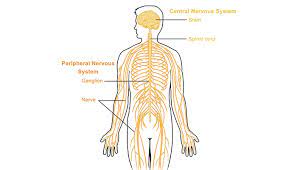
- Central nervous system. This includes the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is responsible for activities associated with thinking, emotions, sensory processing, and cognition. The term “central” refers to its position as the primary processing center for information collected from throughout the body.
Examples of neurological conditions impacting the CNS include multiple sclerosis, meningitis, epilepsy, and other seizure disorders, various cancers that cause tumor growth, strokes, cerebral palsy, and more.
- Peripheral nervous system. This includes the multitude of nerves that branch off of the spinal cord. Conditions potentially impacting the peripheral nervous system include diseases caused by viruses (like Guillain-Barre syndrome), nerve compression disorders (like carpal tunnel syndrome), autoimmune diseases (like lupus and rheumatoid arthritis), endocrine (hormone) system disorders like hypothyroidism and diabetes, and more.

The basic unit of the nervous system is called a neuron (nerve cell). Neurons convey electrical impulses across synapses in a chain to coordinate muscle movement, communicate sensory information, and other functions.

Neurological conditions often target neurons and their function at the cellular level, such as, for example, motor neuron diseases (MNDs.
In addition to neurons, the nervous system is also comprised of non-neuron cells called glia. Unlike neurons, glia don’t ferry messages. Instead, they provide logistical support like waste and nutrient transport, neuron insulation, and other functions.
Dysfunctional glia contribute to the development of various neurological conditions like glioblastoma, autism, psychiatric disorders, Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis.

What Is the Clinical Definition of a Neurological Condition?
Different medical organizations offer slightly different and nuanced definitions of what is meant by a “neurological condition.” Here is how the World Health Organization, viewed by many as the definitive global medical authority, defines the term:
“Diseases of the central and peripheral nervous system. In other words, the brain, spinal cord, cranial nerves, peripheral nerves, nerve roots, autonomic nervous system, neuromuscular junction, and muscles.”
Neurological conditions don’t affect the brain alone or even just the nervous system. Because the nervous system is closely involved in every major function of the body, the impacts of an untreated neurological condition can be devastating on multiple fronts. Even “mild” neurological disease can severely negatively impact quality of life (QOL).
The possible symptoms of neurological conditions, in both children and adults, are wide-ranging and can include but are by no means limited to:
- muscle weakness
- seizures
- confusion
- paralysis
- pain
- altered consciousness
- poor coordination
- loss of sensation
- depression
- anxiety
- mood disorders
The above symptoms range in severity from mild to potentially life-threatening. They can be either physical or mental in nature.
Examples of Neurological Conditions
There are literally thousands of diagnosable neurological conditions and their various sub-types. Here is a brief list of the more common neurological conditions* prevalent in the population today:
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
- Ataxia
- Bell’s Palsy
- Brain Tumors
- Epilepsy and Seizures
- Headache
- Head Injury
- Hydrocephalus
- Meningitis
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Muscular Dystrophy
- Stroke
*Again, this is by no means an exhaustive list of the many varieties and sub-varieties of neurological conditions.
How Are Neurological Conditions Treated?
The brain, along with the other components of the neurological system, is incredibly complex. As such,, conditions that affect it are often challenging to treat.
The treatment for any given neurological condition will depend on the diagnosis, the severity of the illness, how far the disease has progressed, the individual health status of the patient, and other unique factors.
Some neurological conditions can be cured while others, as of 2022, are as of yet incurable. Those can only be managed to slow the progression and mitigate symptoms.
However, given the increasingly rapid pace of technological innovation and a progressively improved understanding of the complex nervous system, there is cause for hope. We can expect major developments in treating, curing, and potentially reversing the damage caused by currently incurable neurological conditions in the years to come.
The main treatment and intervention strategies for neurological conditions include:
- Neurorehabilitation
- Physiotherapy to manage relevant symptoms
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT)
- Lifestyle changes
- Therapeutics/medications
- Pain management techniques
- Surgery
- Diet optimization
- Sleep optimization
Neurologists treating neurological disease typically employ a combination of the above strategies to promote healing on multiple fronts. Typically, doctors move from least invasive treatment modalities to more invasive as necessary to limit undesirable side effects from treatment.
Researchers and clinicians regularly discover effective new breakthrough interventions to treat neurological disorders, which is why seeking care from an advanced, leading neurology clinic is so important to achieve the best possible outcomes based on the latest science.
Contact Child Neurology Center of Northwest Florida
Child Neurology Center of Northwest Florida devotes our state-of-the-art equipment and techniques, as well as our extensive clinical experience, to fully treating every child who enters our doors.
We’re proud to have served the Northwest Florida region since 2001, when founder and Pensacola native Dr. Ben Renfroe first opened our doors to treat patients with our unique and aggressive approach to medicine. We’re also a stone’s throw away from Mobile and surrounding areas.
You are always welcome to contact us to make an appointment at our expert-staffed, cutting-edge child neurology center at 400 Gulf Breeze Parkway, Suite 300 in Gulf Breeze.